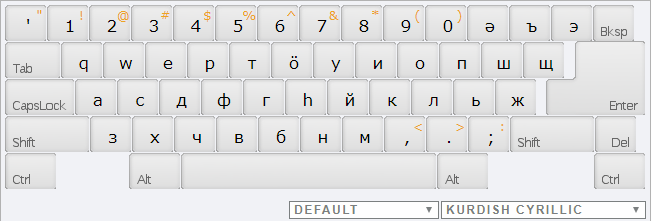
KURDISH
Kurdish Script uppercase normal
А Б В Г Г’ Д Е Ә Ә’ Ж З И Й К К’ Л М Н О Ö
П П’ Р Р’ С Т Т’ У Ф Х һ һ’ Ч Ч’ Ш Щ Ъ Э Q W
Kurdish Script uppercase italic
А Б В Г Г’ Д Е Ә Ә’ Ж З И Й К К’ Л М Н О Ö
П П’ Р Р’ С Т Т’ У Ф Х һ һ’ Ч Ч’ Ш Щ Ъ Э Q W
Kurdish Script lowercase normal
а б в г г’ д е ә ә’ ж з и й к к’ л м н о ö
п п’ р р’ с т т’ у ф х h h’ ч ч’ ш щ ъ э q w
Kurdish Script lowercase italic
а б в г г’ д е ә ә’ ж з и й к к’ л м н о ö
п п’ р р’ с т т’ у ф х h h’ ч ч’ ш щ ъ э q w
Kurdish Language on Wikipedia
WIKIPEDIA
The Kurdish languages are written in either of two alphabets: a Latin alphabet introduced by Jeladet Ali Bedirkhan (Celadet Alî Bedirxan) in 1932 (Bedirxan alphabet, or Hawar after the Hawar magazine), and a Persian alphabet-based Soriani alphabet, named for the historical Soran Emirate of present-day Iraqi Kurdistan. The Kurdistan Regional Government (KRG) has agreed upon a standard for Soriani, implemented in Unicode for computation purposes.
The Hawar is used in Turkey, Syria and Armenia; the Soriani in Iraq and Iran. Two additional alphabets, based on the Armenian alphabet and the Cyrillic script, were once used in Armenian Soviet Socialist Republic.
A Cyrillic script is used for the few (Kurmanji-speaking) Kurds in the former Soviet Union, especially in Armenia, consisting of 40 letters. It was designed in 1946 by Heciyê Cindî.
OSSETIC
Ossetic Script uppercase normal
А Æ Б В Г ГЪ Д ДЗ Е Ё Ж З И Й К КЪ Л М Н О
П ПЪ Р С Т ТЪ У Ф Х ХЪ Ц ЦЪ Ч ЧЪ Ш Щ Ъ Ы Ь Э Ю Я
Ossetic Script uppercase italic
А Æ Б В Г ГЪ Д ДЗ Е Ё Ж З И Й К КЪ Л М Н О
П ПЪ Р С Т ТЪ У Ф Х ХЪ Ц ЦЪ Ч ЧЪ Ш Щ Ъ Ы Ь Э Ю Я
Ossetic Script lowercase normal
а æ б в г гъ д дз е ё ж з и й к къ л м н о
п пъ р с т тъ у ф х хъ ц цъ ч чъ ш щ ъ ы ь э ю я
Ossetic Script lowercase italic
а æ б в г гъ д дз е ё ж з и й к къ л м н о
п пъ р с т тъ у ф х хъ ц цъ ч чъ ш щ ъ ы ь э ю я
Di- and tri-graphs are not officially letters of the alphabet, but are listed here to represent phonemically distinctive sounds.
The letters ё, ж, ш, щ, ь, э, ю, я (and also ъ outside the digraphs) are used only in borrowings. The letter у denotes simultaneously 2 phonemes – [y] and [ў]. The digraphs къ, пъ, тъ, цъ, чъ denote glottalized (abruptive) sounds, гъ is the uvular sonorous trembling consonant, хъ is the uvular deaf consonant, дж, дз are affricates; ligature ӕ – anterior wide broad vowel.
Ossetia
[oss] Severnaya Osetiya-Alaniya and Kabardino-Balkariya; north of Ossetic in Georgia. 451,000 in Russian Federation (2010 census). Population total all countries: 569,650. Ethnic population: 529,000 (2010 census). Status: 5 (Developing). Statutory language of provincial identity in North Ossetia-Alania (1993, Constitution, Article 68(2)). Alternate Names: Osetin, Ossetian Dialects: Digor, Iron. Classification: Indo-European, Indo-Iranian, Iranian, Eastern, Northeastern Comments: Christian (Orthodox), Muslim (Sunni).Source of information: Languages of the World | Russian Federation
Ossetic Language on Wikipedia
Осетинская письменность on Wikipedia
Ossetic Language – examples
Осетинский язык он-лайн: учебные и справочные материалы
Omniglot: Ossetian (ирон ӕвзаг / дигорон ӕвзаг)
TAJIK
Tajik Script uppercase normal
А Б В Г Д Е Ё Ж З И Й К Л М Н О
П Р С Т У Ф Х Ц Ч Ш Щ Ъ Ы Ь Э Ю Я Ғ Ӣ Қ Ӯ Ҳ Ҷ
Tajik Script uppercase italic
А Б В Г Д Е Ё Ж З И Й К Л М Н О
П Р С Т У Ф Х Ц Ч Ш Щ Ъ Ы Ь Э Ю Я Ғ Ӣ Қ Ӯ Ҳ Ҷ
Tajik Script lowercase normal
а б в г д е ё ж з и й к л м н о
п р с т у ф х ц ч ш щ ъ ы ь э ю я ғ ӣ қ ӯ ҳ ҷ
Tajik Script lowercase italic
а б в г д е ё ж з и й к л м н о
п р с т у ф х ц ч ш щ ъ ы ь э ю я ғ ӣ қ ӯ ҳ ҷ
A language of Tajikistan
ISO: 639-3tgk
Alternate Names: Tadzhik, Tajik, Tajiki Persian, “Galcha” (pej.)
Autonym: тоҷикӣ (Tojiki)
Population: 6,380,000 (2012 UNSD). Ethnic population: 6,370,000 (2010 census). Total users in all countries: 7,863,920.
Location: Widespread.
Language Maps: Kyrgyzstan and Tajikistan, Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan
Language Status: 1 (National). Statutory national language (1994, Constitution, Article 2).
Classification: Indo-European, Indo-Iranian, Iranian, Western, Southwestern, Persian
Dialects: 4 groups of small dialects; no distinct boundaries. Dialect blending into Dari Persian [prs] in Afghanistan.
Typology: SOV; verb affixes mark person, number; tense and aspect; causatives; 27 consonant and 6 vowel phonemes; nono-tonal; stress on final syllable.
Language Use: Also use Northern Uzbek [uzn], Russian [rus].
Language Development: Literature. Radio. Bible: 1992–1999.
Language Resources: OLAC resources in and about Tajiki
Writing: Arabic script, Naskh variant [Arab], used until 1928. Cyrillic script [Cyrl], used since 1940, primary usage. Hebrew script [Hebr], used by Bukharan Jews. Latin script [Latn], used from 1928–1940.
Other Comments: Russian sources refer to Persian dialects in Afghanistan as Tajiki. So-called Tajiki in China is actually Shugni [sgh] or Wakhi [wbl]. Some Tajiki-speaking Roma communities in Russian central Asia. Muslim.
Source of information: Languages of the World | A language of Tajikistan