Class substitution
feature locl {
script cyrl;
language BGR exclude_dflt;
sub @locl3 by @locl4;
# This is a comment.
# @locl3: uni0414 uni0418 uni0419 uni040D uni041B uni0424 uni0432 uni0433 uni0434 uni0436 uni0437 uni0438 uni0439 uni045D uni043A uni043B uni043D uni043F uni0442 uni0447 uni0446 uni0448 uni0449 uni044C uni044A uni044E
# @locl4: uni0414.loclBGR uni0418.loclBGR uni0419.loclBGR uni040D.loclBGR uni041B.loclBGR uni0424.loclBGR uni0432.loclBGR uni0433.loclBGR uni0434.loclBGR uni0436.loclBGR uni0437.loclBGR uni0438.loclBGR uni0439.loclBGR uni045D.loclBGR uni043A.loclBGR uni043B.loclBGR uni043D.loclBGR uni043F.loclBGR uni0442.loclBGR uni0447.loclBGR uni0446.loclBGR uni0448.loclBGR uni0449.loclBGR uni044C.loclBGR uni044A.loclBGR uni044E.loclBGR
} locl;
Unicode name to Unicode name substitution
feature locl {
script cyrl;
language BGR exclude_dflt;
sub [uni0414 uni0418 uni0419 uni040D uni041B uni0424 uni0432 uni0433 uni0434 uni0436 uni0437 uni0438 uni0439 uni045D uni043A uni043B uni043D uni043F uni0442 uni0447 uni0446 uni0448 uni0449 uni044C uni044A uni044E] by [uni0414.loclBGR uni0418.loclBGR uni0419.loclBGR uni040D.loclBGR uni041B.loclBGR uni0424.loclBGR uni0432.loclBGR uni0433.loclBGR uni0434.loclBGR uni0436.loclBGR uni0437.loclBGR uni0438.loclBGR uni0439.loclBGR uni045D.loclBGR uni043A.loclBGR uni043B.loclBGR uni043D.loclBGR uni043F.loclBGR uni0442.loclBGR uni0447.loclBGR uni0446.loclBGR uni0448.loclBGR uni0449.loclBGR uni044C.loclBGR uni044A.loclBGR uni044E.loclBGR];
} locl;

HTML Language Code Reference
The HTML lang attribute can be used to declare the language of a Web page or a portion of a Web page. This is meant to assist search engines and browsers.
According to the W3C recommendation you should declare the primary language for each Web page with the lang attribute inside the tag, like this:
…
</html>
or like this:
…
</html>
The code lang=”en-GB” means English (United Kingdom). The code lang=”en-US” means English (United States). See others language definition codes at GitHub.
In XHTML, the language is declared inside the tag as follows:
…
</html>
HTML Language Code Reference for Russian language
…
</html>
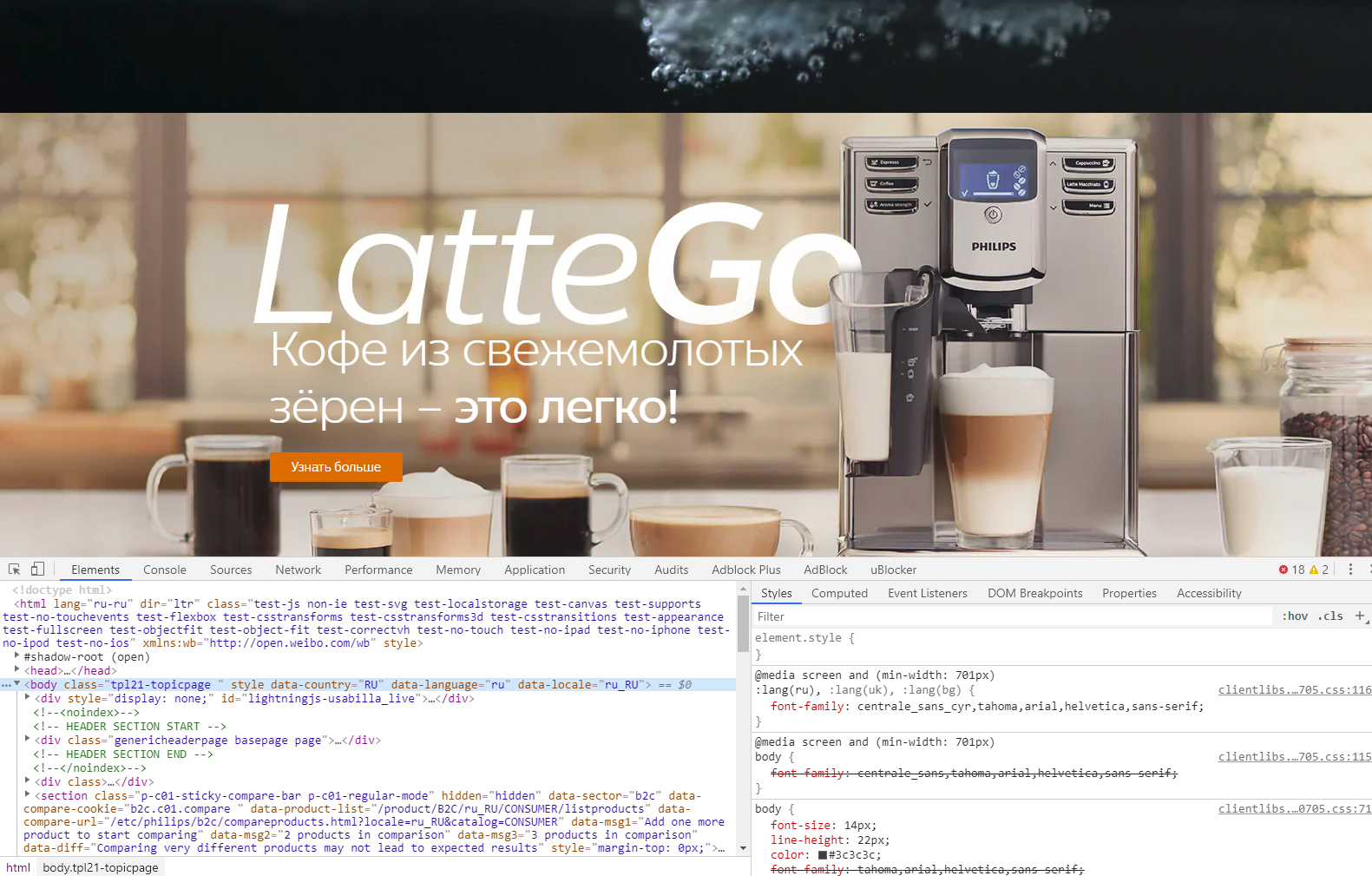
Please click here to see the picture enlarged.
The site use Centrale Sans font by Alexander Nedelev and Veronika Slavova, Typedepot
Notice that it doesn’t matter whether the language in the HTML page is really Russian or other one.
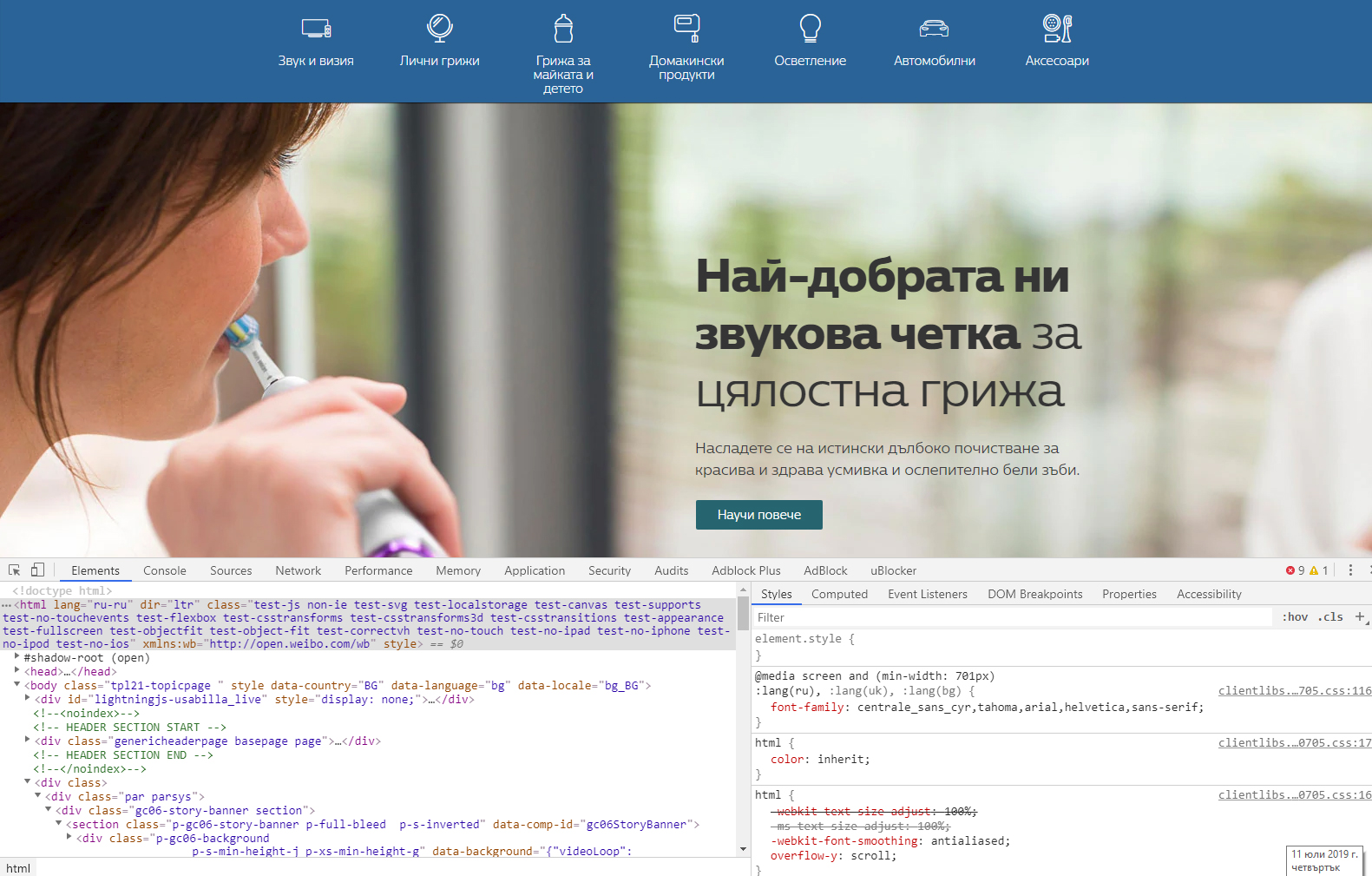
Please click here to see the picture enlarged.
The site use Centrale Sans font by Alexander Nedelev and Veronika Slavova, Typedepot
HTML Language Code Reference for Bulgarian language
…
</html>
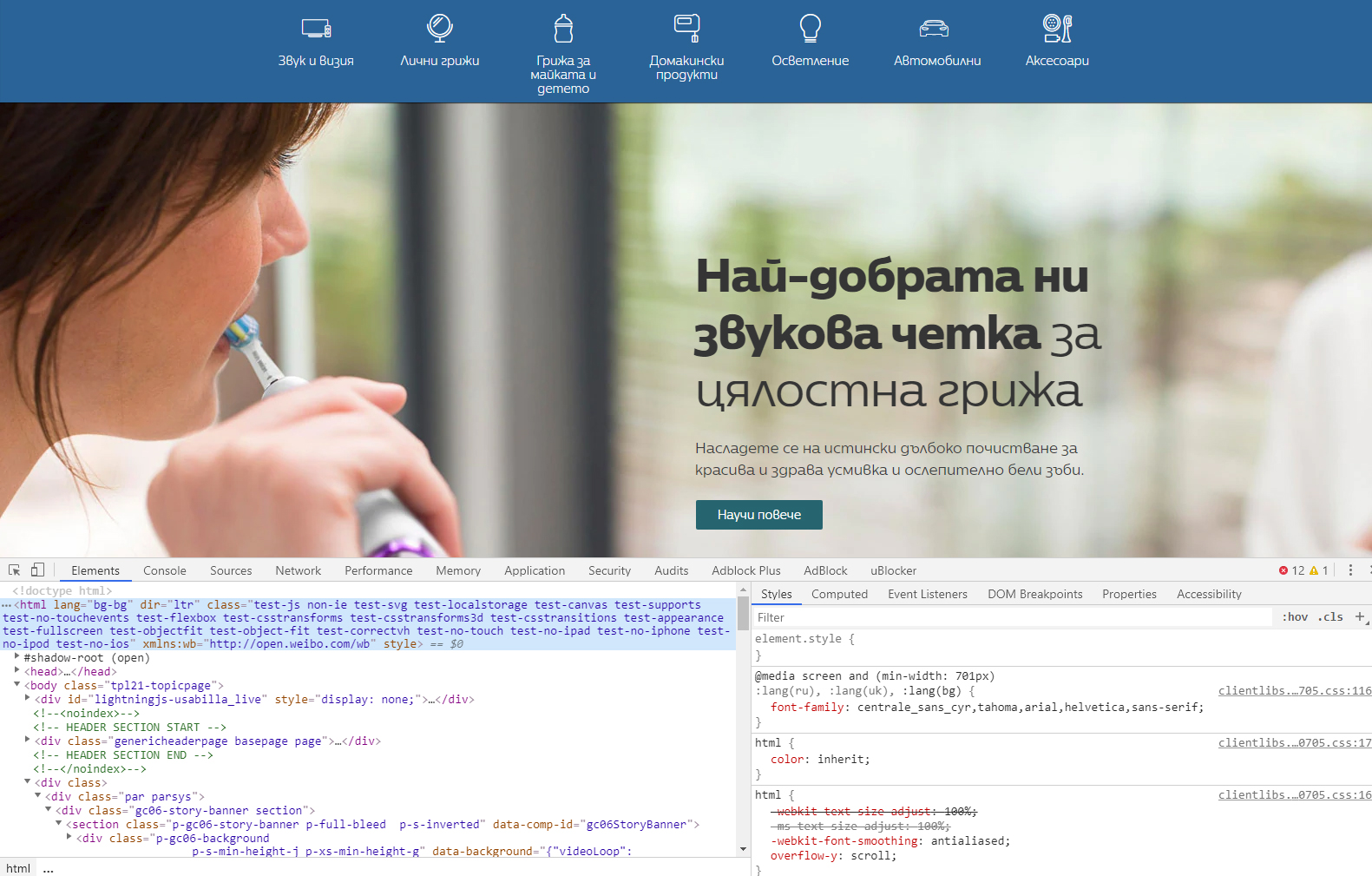
Please click here to see the picture enlarged.
The site use Centrale Sans font by Alexander Nedelev and Veronika Slavova, Typedepot
HTML Mixed Language Code Reference
You can use language code reference on a portion of a Web page either.
…
</p>
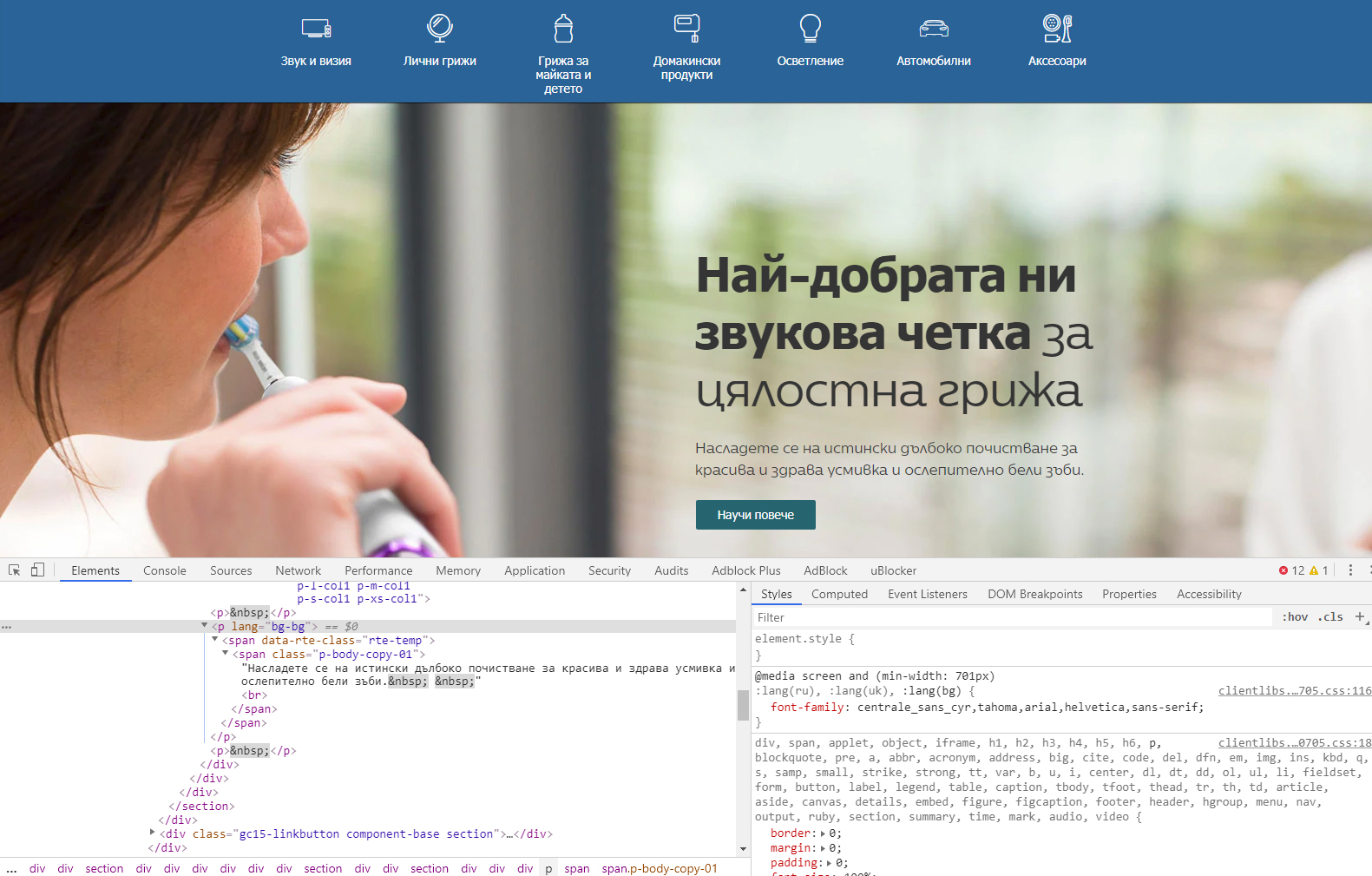
Please click here to see the picture enlarged.
The site use Centrale Sans font by Alexander Nedelev and Veronika Slavova, Typedepot
…
</span>
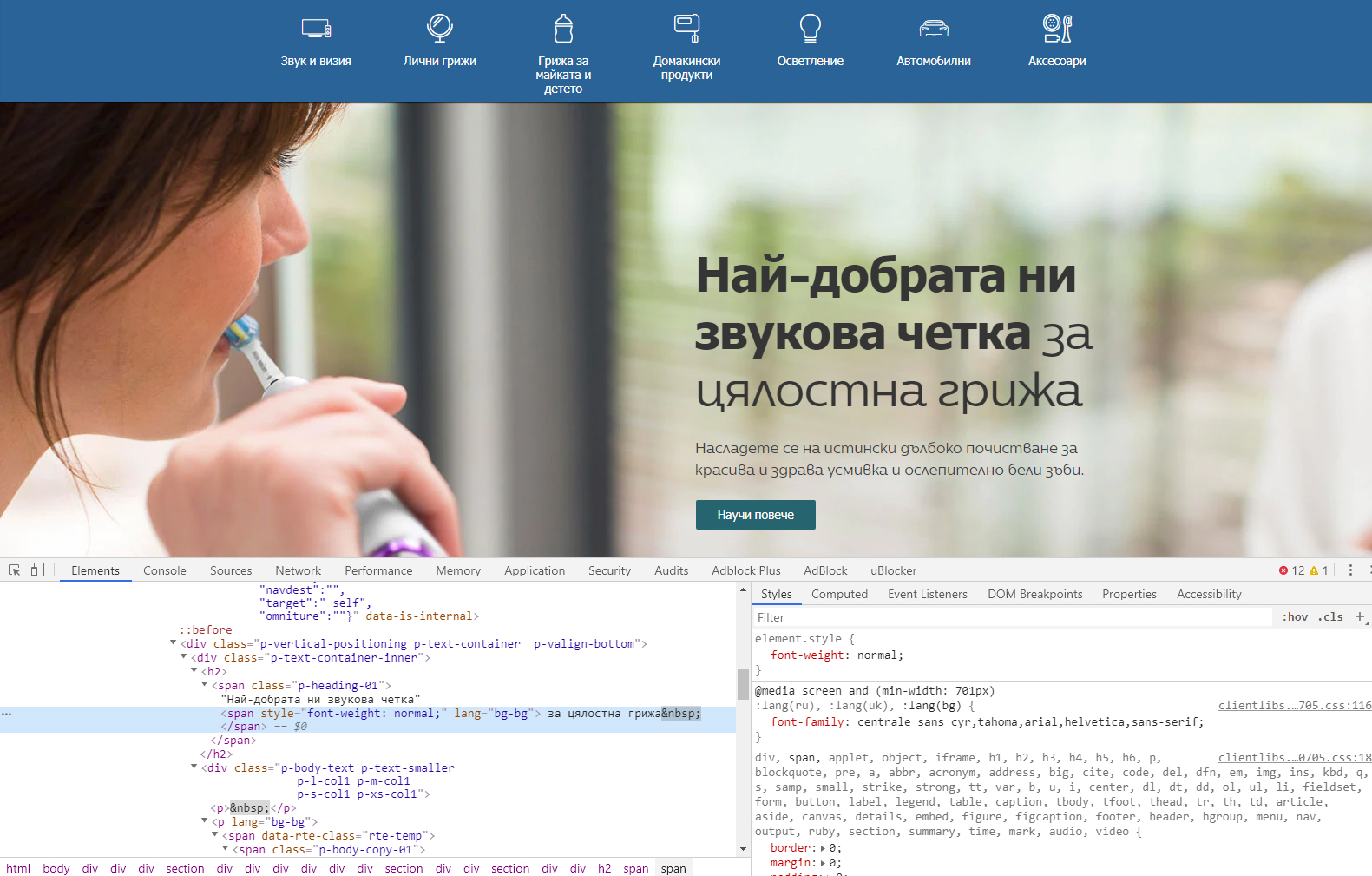
Please click here to see the picture enlarged.
The site use Centrale Sans font by Alexander Nedelev and Veronika Slavova, Typedepot
Other sources
Tags: Language System Tags
OpenType: Local Features (OpenType code)
Fontfabric: A closer look at the Bulgarian stylistic variation of the Cyrillic script
Todor Georgiev: The Cyrillic Alphabet Yesterday, Today, and Tomorrow
Krasen Krastev: Bulgarian Cyrillic as a Mark of Identity. “Culture” Magazine. Issue 20
Eugene Yukechev: On the appearance and development of Cyrillic letterforms
Glyphs Forum: Multiple identical (cyrillic) glyphs in Font
Glyphs Forum: Local Feature for Bulgarian Cyrillic?
Lettersoup: What shall be done for Bulgarian Cyrillic .loclBGR